Orthogonal separation by chromatography is crucial to an effective downstream purification process for biotherapeutics. Heuristically, chromatographic steps that employ different modalities of interaction, such as ion exchange (IEX) or hydrophobic interaction (HIC), are believed to be orthogonal. However, the degree of orthogonal separation is seldom quantified, which may overlook opportunities for synergistic separation across different chromatographic resin pairs or sequences.
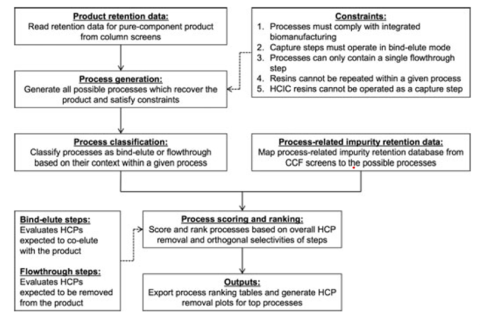
To address this gap, we have developed novel metrics for quantifying orthogonality between any resin pair in the context of removing product and process-related impurities. We then integrated these metrics with in-silico techniques to facilitate analysis of large screening studies while enabling a knowledge-based approach to identify globally optimal resin pairs for a given separation challenge.
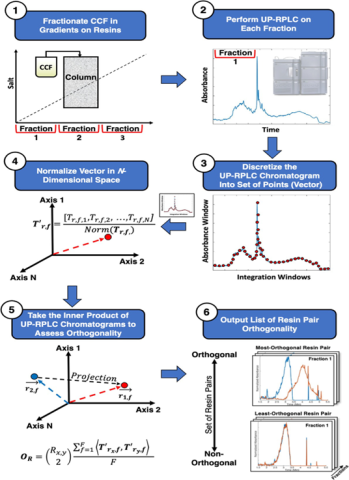
We have employed this in-silico mediated workflow to expedite the development of highly separable and orthogonal 3-step chromatographic processes for the removal of HCPs from Pichia pastoris-derived human growth hormone (hGH) and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)1. Expanding on this work, we adapted this framework to rapidly identify optimal processes for removing both process and product-related impurities from Pichia pastoris-derived Interferon alpha-2b (IFN-α2b)2. For these works, we developed a novel reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) analytical method to perform fingerprint analysis of process-related impurities during the resin screens to enable orthogonality calculations. By combining the orthogonality metric with in-silico techniques, optimal downstream purification processes for non-platform products were developed in 2-3 weeks from simple linear gradient screening experiments. These works have also shown that the in-silico framework can be translated to various application spaces and separation challenges.
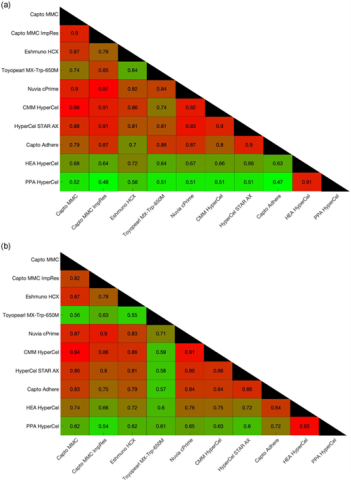
On top of process development, the in-silico framework has been utilized to elucidate our understanding of orthogonality as well. To investigate true resin pair orthogonality or orthogonality in the lack of a purification objective, we have utilized the in-silico framework to compare the orthogonal resin pairs for process-related impurities between two expression systems: Pichia pastoris and Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO)3. The results showed that different resin pairs were orthogonal depending on the expression system, which suggested that orthogonality was context dependent. Therefore, to investigate orthogonality in the absence of context, or product agnostic orthogonality, we screened a pool of biophysically diverse model proteins to determine the truly globally optimal resin pairs4.
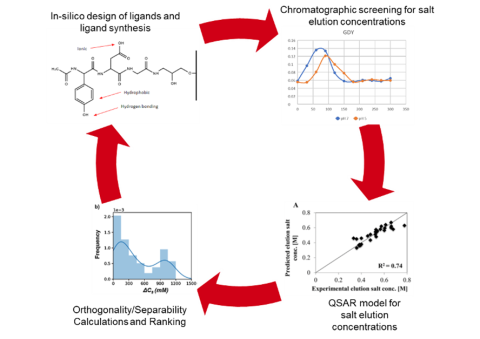
We are continuing our development of the utility of the in-silico framework and expanding upon our understanding of orthogonality by investigating separation challenges for mAb-based therapeutics. Currently, we are using the in-silico framework to identify orthogonal resin sequences for the removal of HCPs from a CHO-derived mAb product and for the removal of multiple classes of product-related impurities from CHO-derived mAb, Fc-Fusion, and Fab products. We aim to enhance the in-silico framework to include column modeling to bring process optimization into the in-silico space. To bring in a mechanistic understanding of orthogonality, we can conduct proteomic analysis to identify the specific impurities being removed by orthogonal resin pairs. We can then use these insights on orthogonality to inform novel ligand design.
Selected References:
1. Timmick, S. M. et al. An impurity characterization based approach for the rapid development of integrated downstream purification processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 115, 2048–2060 (2018).
2. Vecchiarello, N. et al. A combined screening and in silico strategy for the rapid design of integrated downstream processes for process and product-related impurity removal. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 116, 2178–2190 (2019).
3. Vecchiarello, N., Timmick, S. M. & Cramer, S. A framework for calculating orthogonal selectivities in multimodal systems directly from cell culture fluid. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 119, 299–314 (2022).
4. Bilodeau, C. L., Vecchiarello, N. A., Altern, S. & Cramer, S. M. Quantifying Orthogonality and Separability: A Method for Optimizing Resin Selection and Design. J. Chromatogr. A 461429 (2020) doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461429.