Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship (QSAR) is a powerful predictive tool connecting the experimental behaviors (e.g. retention in chromatography, solubility etc.) to physiochemical properties of molecules (e.g. charge density, hydrophobic surface area, etc.). It is also known as structure activity relationship (SAR), quantitative structure property relationship (QSPR) or quantitative structure retention relationship (QSRR).
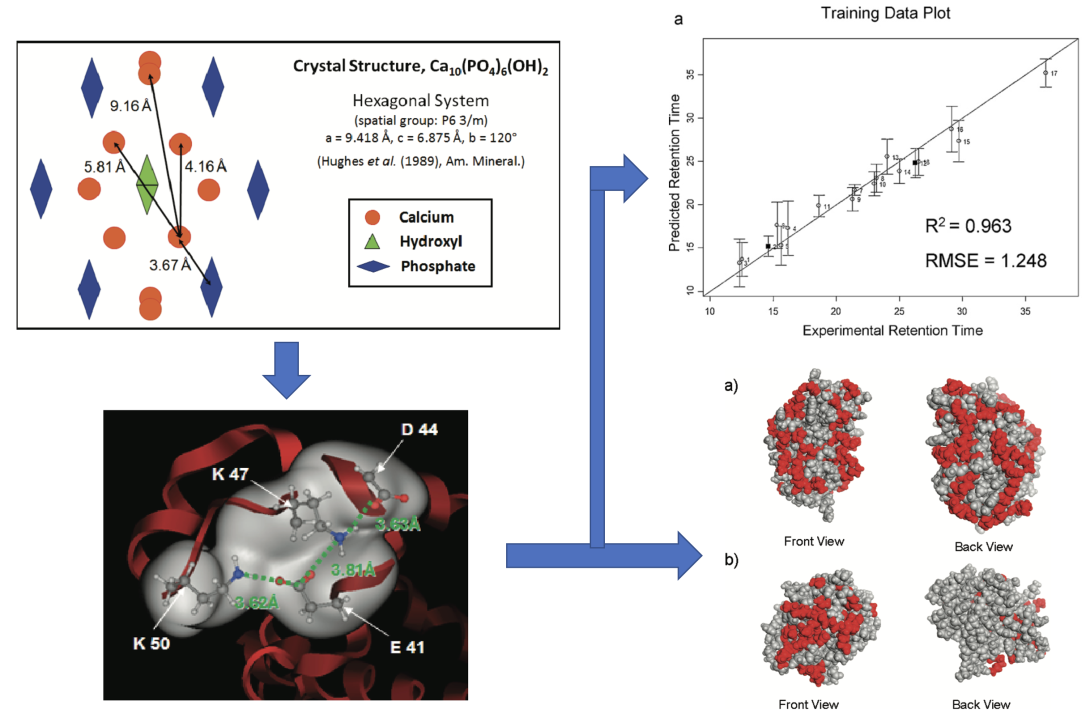
Figure 1. Fundamental of QSAR
Utilizing fundamental insights for protein-ligand interactions or protein-protein interactions, series of numerical descriptors based on sequences or 3D structures of molecules are generated as inputs for predictive models. A variety of machine-learning methods ( e.g. linear models, SVM, tree-based, neural network etc.) can be applied here to predict the activities using selected descriptors. Classification and/or regression model will then be developed to get a prior estimate of experimental behaviors for similar molecules.
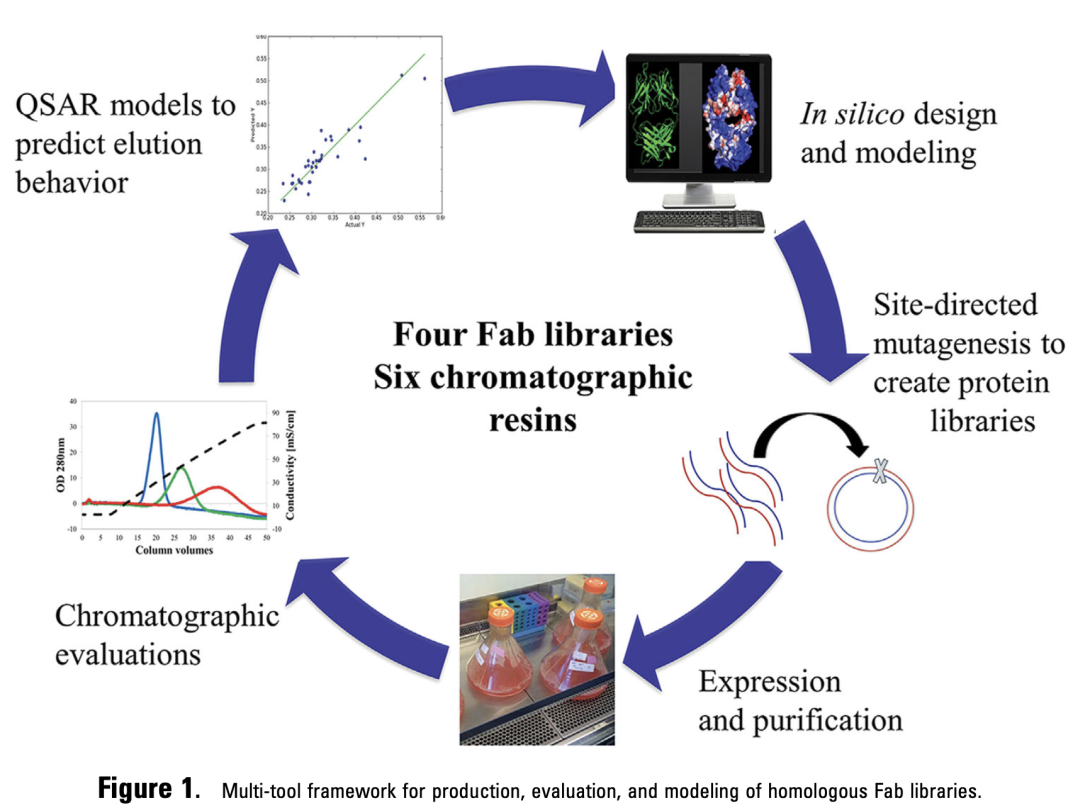
Figure 2. Fab library
Previously, our lab have developed a wide variety of predictive models for different chromatography systems (reverse phase, IEX, HIC, hydroxyapatite, multimodal etc.)1-6 and mAb biophysical property (solubility)7. In addition, we have also dedicated into developing novel protein and ligand descriptors based on fundamental understanding gained from MD simulations. Combining with state-of-art machine learning algorithms and high-throughput screening technique, we were hoping to develop robust predictive tools to facilitate expedited process development.
(Cr: Dr. Han Xuan)
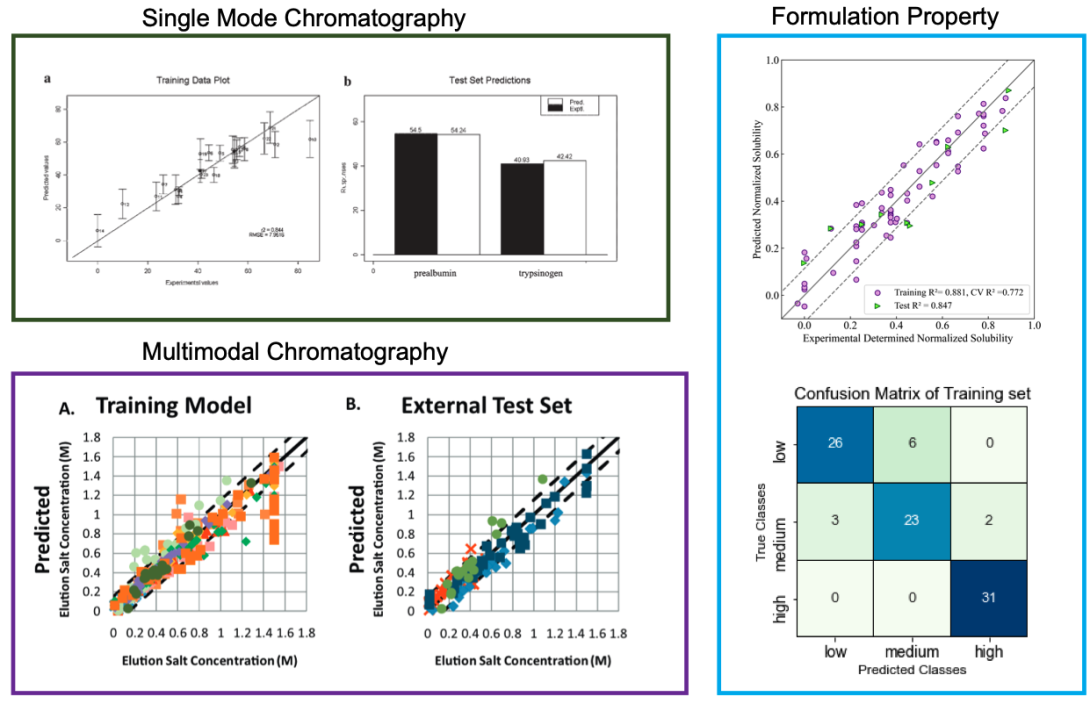
Figure 3. Various previous QSAR model
Selected References
1. C. B. Mazza, N. Sukumar, C. M. Breneman, S. M. Cramer, Prediction of protein retention in ion-exchange systems using molecular descriptors obtained from crystal structure. Anal. Chem. 73(22), 5457–5461 (2001).
2. A. Ladiwala, F. Xia, Q. Luo, C. M. Breneman, S. M. Cramer, Investigation of protein retention and selectivity in HIC systems using quantitative structure retention relationship models. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 93(5), 836–850 (2006).
3. Y. Hou, C.J. Morrison and S .M. Cramer. Classification of Protein Binding in Hydroxyapatite Chromatography: Synergistic Interactions on the Molecular Scale. Anal. Chem. (2011)
4. Y. Hou, S. M. Cramer, Evaluation of selectivity in multimodal anion exchange systems: A priori prediction of protein retention and examination of mobile phase modifier effects. J. Chromatogr. A 1218(43), 7813–7820 (2011).
5. J. A. Woo, et al., Defining the property space for chromatographic ligands from a homologous series of mixed-mode ligands. J. Chromatogr. A 1407, 58–68 (2015).
6. J. R. Robinson, H. S. Karkov, J. A. Woo, B. O. Krogh, S. M. Cramer, QSAR models for prediction of chromatographic behavior of homologous Fab variants: QSAR Models for Fab Variants. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 114(6), 1231–1240 (2017).
7. X. Han, J. Shih, Y. Lin, Q. Chai, S. M. Cramer, Development of QSAR models for in silico screening of antibody solubility. mAbs 14(1), 1–13 (2022).